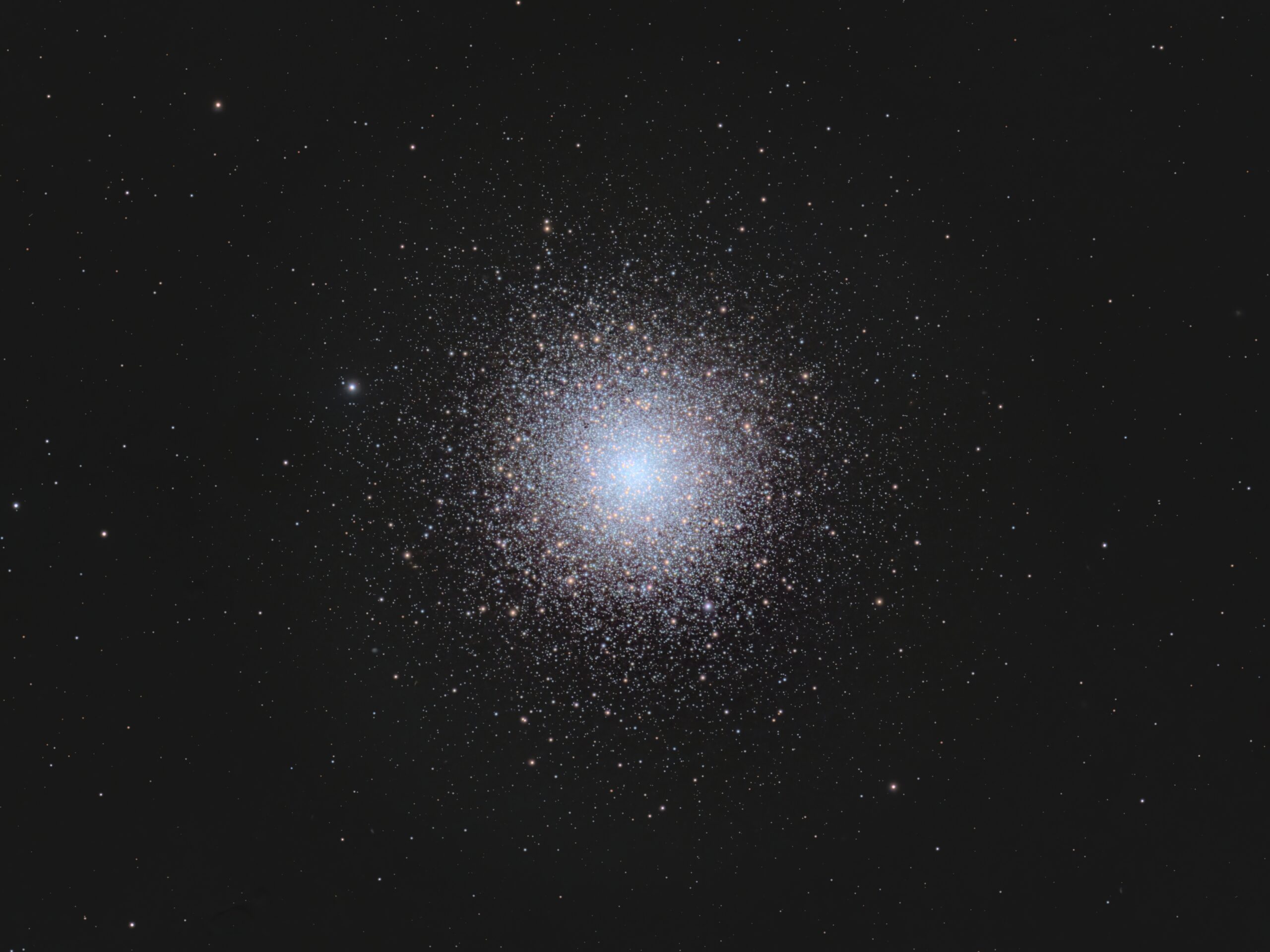
Messier M92

Click image for full size version
August 5, 2024
Globular cluster Messier 92 (M92) lies in Hercules, not far from M13, which usually gets more attention from both visual observers and imagers. M92 is one of my favourite telescope targets, especially in my 20″ reflector. It lies about 26,700 light years away from us, and appears a little less than half the width of the full Moon. Its mass is about 200,000 times that of the Sun, and its age is estimated at 14 billion years.
I’ve shot this cluster several times, most recently in 2021 with 6″and a 4″ refractors.
Tekkies:
Acquisition, focusing, and control of Paramount MX mount with N.I.N.A., TheSkyX. Guiding with PHD2. Primalucelab low-profile 2″ Essato focuser and ARCO rotator. Equipment control with PrimaLuce Labs Eagle 4 Pro computer. All pre-processing and processing in PixInsight. Acquired from my SkyShed in Guelph. Data acquired under little to no moonlight, good transparency and average seeing on the night of July 31-August 1, 2024.
Celestron 14″ EDGE HD telescope at f/11 (3,912 mm focal length) and QHY600M camera binned 2×2 with Optolong filters.
15 x 5m and 15 x 1m Red = 1hr 30m
16 x 5m and 14 x 1m Green = 1hr 34m
15 x 5m and 14 x 1m Blue = 1hr 29m
Total: 4hr 33m
Preprocessing: The WeightedBatchPreProcessing script was used to perform calibration, cosmetic correction, weighting, registration, local normalization, and integration of all frames. The 60s and 300s frames were integrated together into one master for each filter.
RGB master: An RGB image was made from the Red, Green and Blue masters using ChannelCombination in RGB mode.
Synthetic Luminance: A SynthL was made by integrating the three masters, weighted by SNR, with no pixel rejection.
Gradient Removal: DBE was used to remove gradients from the RGB and SynthL masters.
Colour Calibration: ColorCalibration was used to calibrate the RGB master.
Deconvolution: BlurXterminator was applied to the RGB and SynthL masters with Automatic psf , star sharpening set to 0.5, and non-stellar set to 0.5.
Linear Noise Reduction: NoiseXterminator was applied to the RGB and SynthL masters with settings Amount=0.9 and Detail=0
Stretching: ArcsinHStretch followed by HistogramTransformation was applied to the RGB and SynthL masters to make pleasing images. Approximate background level after stretch was 0.1 for SynthL and 0.09 for RGB.
Nonlinear Processing
Combining SynthL and RGB: LRGBCombination was used to replace the lightness channel of the RGB image with the SynthL.
Nonlinear Noise Reduction: NoiseXterminator was used to reduce noise in the background areas of the SynthRGB master with Amount=0.9 and Detail=0.15.
Re-stretch: HistogramTransformation was used to boost contrast by moving the dark point to the toe of the histogram and slightly decreasing the mid-point slider.
Halo reduction: A copy of the image was made and processed with the Halo-B-Gon script by Seti Astro using a mask to protect the brighter parts of the globular cluster.
Final Steps: Background, globular cluster, and star brightness, contrast, hue, and saturation were adjusted in several iterations using CurvesTransformation with masks as required. ICCProfileTransformation (sRGB IEC61966-2.1; Relative Colorimetric with black point compensation) was applied prior to saving as a jpg. The finder chart was made using the FindingChart process.






Leave A Comment