NGC 5466
 Click image for full size version
Click image for full size version
May 28, 2024
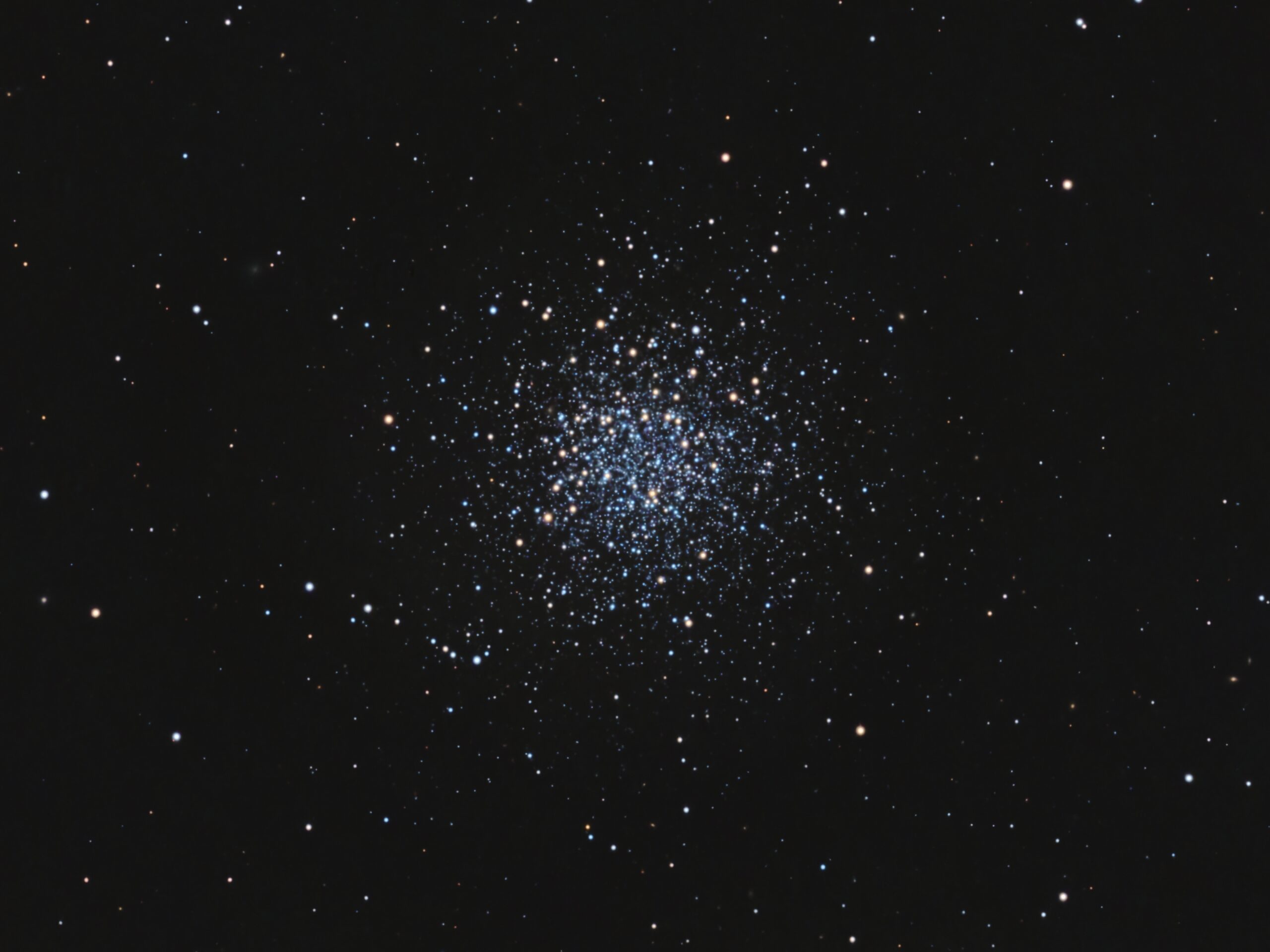
NGC 5466 is an ancient globular cluster. Its age is currently estimated to be 12.88 billion years. It lies about 52,000 light years from us in the constellation Boötes, and about the same distance from the centre of the Milky Way. Unlike some of its very splashy cousins, NGC 5466 has a relatively unconcentrated core. It belongs to Class 12 (the most sparse) of the Shapley-Sawyer Concentration Class for describing the 150 or so Milky Way globular clusters. By comparison, Messier 3 belongs to Class 6, and appears much more densely packed with stars than its more sparse cousin.
NGC 5466 is unusual in containing a particular type of blue star (“horizontal branch”). There are several galaxies scattered throughout the image. All are in the background, much farther away than NGC 5466. It is thought that most galaxies have their own groups of attendant globular clusters.
Tekkies:
Acquisition, focusing, and control of Paramount MX mount and other equipment with N.I.N.A. and TheSkyX. Guiding with PHD2. Primalucelab low-profile 2″ Essato focuser and ARCO rotator. Equipment control with PrimaLuce Labs Eagle 4 Pro computer. All pre-processing and processing in PixInsight. Acquired from my SkyShed in Guelph. Data acquired under little to no moonlight and average transparency and seeing April 24-25, 2024.
Celestron 14″ EDGE HD telescope at f/11 (3,912 mm focal length) and QHY600M camera binned 2×2 with Optolong filters.
55 x 1m Red = 0hr 55m
51 x 1m Green = 0hr 51m
53 x 1m Blue = 0hr 53m
Total: 2hr 39m
Preprocessing: The WeightedBatchPreProcessing script was used to perform calibration, cosmetic correction, weighting, registration, integration and Drizzle integration of all frames.
RGB master: A master RGB image was made from the Red, Green and Blue Drizzled masters using ChannelCombination in RGB mode.
Gradient Removal: DBE was used to remove gradients from the master.
Colour Calibration: ColorCalibration was used to colour-calibrate the master.
Deconvolution: BlurXterminator was applied with Automatic psf , star sharpening set to 0.35, and non-stellar set to 0.5.
Linear Noise Reduction: NoiseXterminator was applied to the RGB master with settings Amount=0.9 and Detail=0.15
Stretching: HistogramTransformation was applied to make a pleasing image. Approximate background level after stretch was 0.1.
Nonlinear Processing
Star Removal: StarXterminator was used to remove the stars from the master, with default settings, except Large Overlap was selected. The stars-only images was retained.
Nonlinear Noise Reduction: NoiseXterminator was used to reduce noise in the background areas of the SynthRGB master with Amount=0.9 and Detail=0.15.
Re-stretch: HistogramTransformation was used to boost contrast by moving the dark point to the toe of the histogram and slightly decreasing the mid-point slider.
Background Smooting: CloneStamp was used to correct a few small defects in the starless image.
Stars-only steps: The CIE L* channel (i.e. the lightness channel) was extracted from the stars-only image was then applied to the star image as a mask. CurvesTransformation’s saturation slider was used to boost colour and brightness in the stars.
Star Restoration: The PixelMath expression combine(starless, stars, op_screen()) was used to combine the starless LHaRGB starless image with the stars-only image.
Final Steps: Background, globular cluster, and star brightness, contrast, hue, and saturation were adjusted in several iterations using CurvesTransformation with masks as required. ICCProfileTransformation (sRGB IEC61966-2.1; Relative Colorimetric with black point compensation) was applied prior to saving as a jpg. The finder chart was made using the FindingChart process.






Very weak because of the cluster magnetudo, but very beautiful the stars. Veery well
Gorgeous!
Great shot. Just love the detail.
Question: Ron, why did you use only an Optolong UV/IP filter as opposed to other more aggressive filters (i.e with NB features)?
globular clusters are broadband targetss so the colours would not look naturaL with a narrowband filter.
Good point. BTW, is this filter essentially just the same as Luminance filter? Or does a Luminance have other optical features?
Essentially the same.