NGC 457 – The Owl Cluster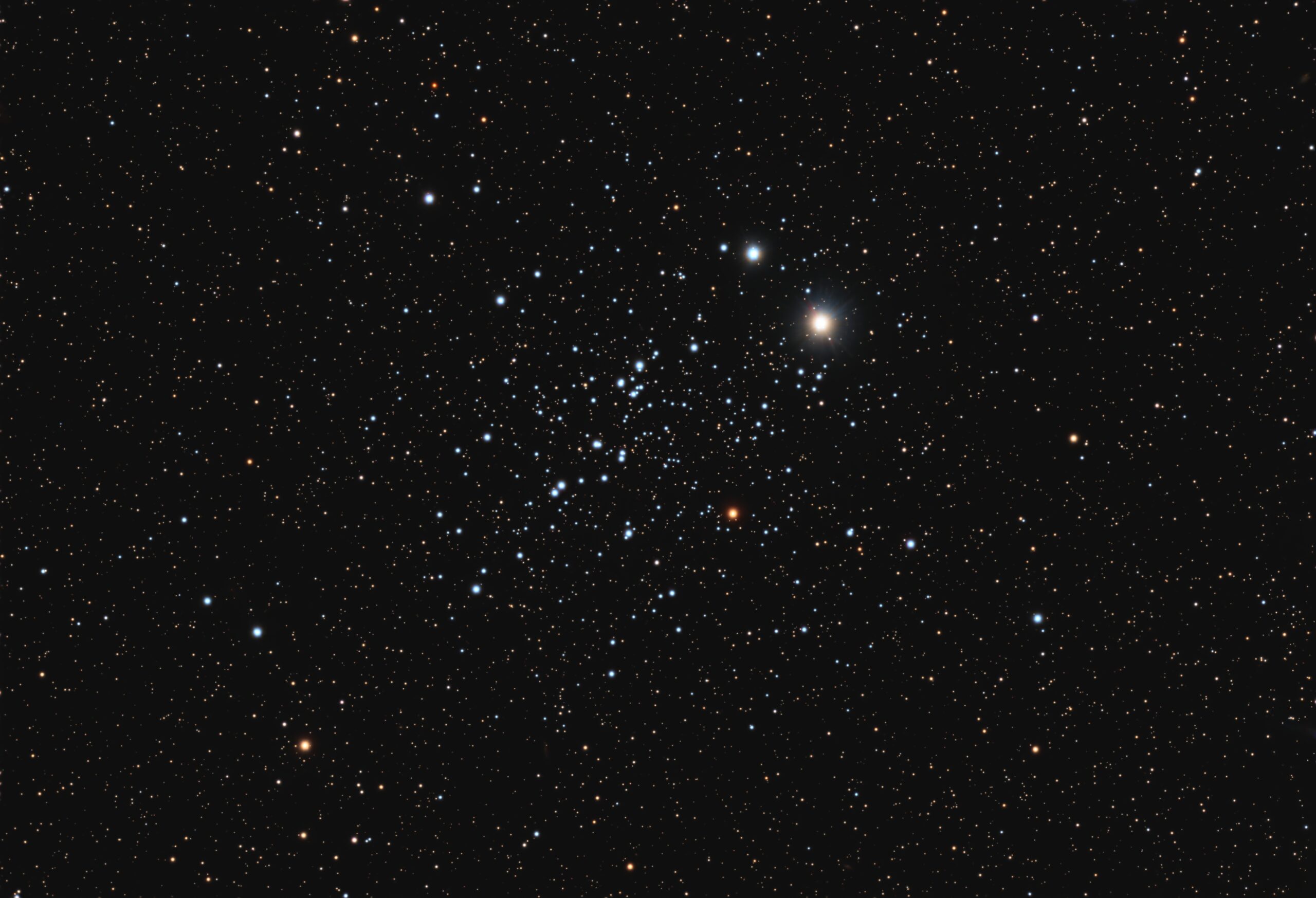
Click image for full size version
December 24, 2024
NGC 457 is the open cluster highlighted in this image. It is about 7,900 light years away and its age is estimated to be 21 million years. It is known as the Owl cluster, the Number 5 Cluster or the E.T. Cluster. I can see the resemblance to the alien from the movie E.T., but to me the owl is more prominent, with wings more than half unfolded.
I have previously posted several images of this object, two of which were published (see here and here). It’s a target I keep coming back to because it is attractive, easy to shoot in a short time, and looks similar to the visual impression in my 20″ Dob. Shooting an object with different optics and cameras helps me in evaluating equipment performance. I am enjoying my current setup very much.
This image was made from less than hour of light all captured on one of the only clear, moonless nights in December 2024.
Tekkies:
Acquisition, focusing, and control of Paramount MX mount with N.I.N.A., TheSkyX. Guiding with PHD2. Primalucelab low-profile 2″ Essato focuser and ARCO rotator. Equipment control with PrimaLuce Labs Eagle 4 Pro computer. All pre-processing and processing in PixInsight. Acquired from my SkyShed in Guelph. Data acquired under moderate moonlight, good transparency and average seeing October 4-21, 2024.
Celestron 14″ EDGE HD telescope at f/11 (3,940 mm focal length) and QHY600M camera binned 2×2 with Optolong filters.
24 x 2m Red = 0hr 48m
27 x 2m Green = 0hr 54m
27 x 2m Blue = 0hr 54m
Total: 2hr 36m
Preprocessing: The WeightedBatchPreProcessing script was used to perform calibration, cosmetic correction, weighting, registration, local normalization, and integration of all frames.
RGB master: An RGB image was made from the Red, Green and Blue masters using ChannelCombination in RGB mode.
Gradient Removal: DBE was used to remove gradients from the RGB master.
Colour Calibration: SpectrophotometricColorCalibration was used to calibrate the RGB master.
Deconvolution: BlurXterminator was applied to the RGB master with Automatic psf , star sharpening set to 0.5, and non-stellar set to 0.
Linear Noise Reduction: NoiseXterminator was applied to the RGB master with settings Amount=0.9 and Detail=0.15
Stretching: HistogramTransformation was applied to the RGB master to make a pleasing image. Approximate background level after stretch was 0.1.
Nonlinear Processing
Star Removal: StarXterminator was used to remove the stars from the RGB master, with default settings.
Nonlinear Noise Reduction: NoiseXterminator was used to reduce noise in the background areas of the RGB master with Amount=0.9 and Detail=0.15.
Background adjustment: CurvesTransformation was used to reduce visibility of bright star haloes in the starless image.
Star Processing and Restoration: CurvesTransformation was applied to the stars-only image through a star mask to boost saturation using the Saturation slider. The stars were then added back into the SHO and HOO master images using the Screen blending mode in PixelMath with the expression combine(starless, RGB_stars, op_screen()).
Final Steps: Background and star brightness, contrast, hue, and saturation were adjusted in several iterations using CurvesTransformation with masks as required. ICCProfileTransformation (sRGB IEC61966-2.1; Relative Colorimetric with black point compensation) was applied prior to saving as a jpg. The finder chart was made using the FindingChart process.






Leave A Comment