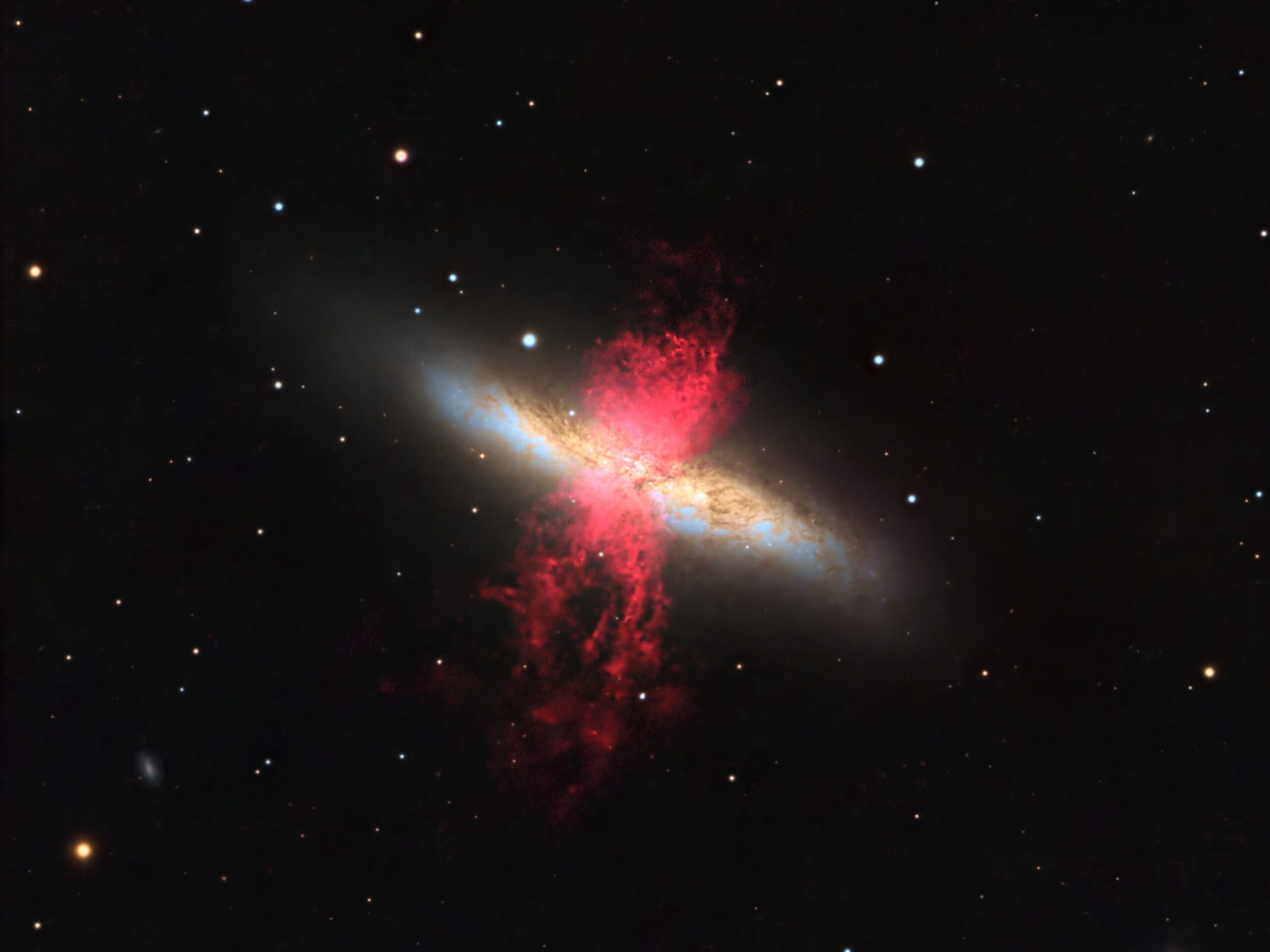
M82
 Click image for full size version
Click image for full size version
March 6, 2024
M82 is a rather famous irregular galaxy in Ursa Major, the Great Bear constellation, which is easily observed through the eyepiece of my 10″ f/6 reflector. Of course visually it is just a grey smudge, not the beautiful, colourful object shown in this image.
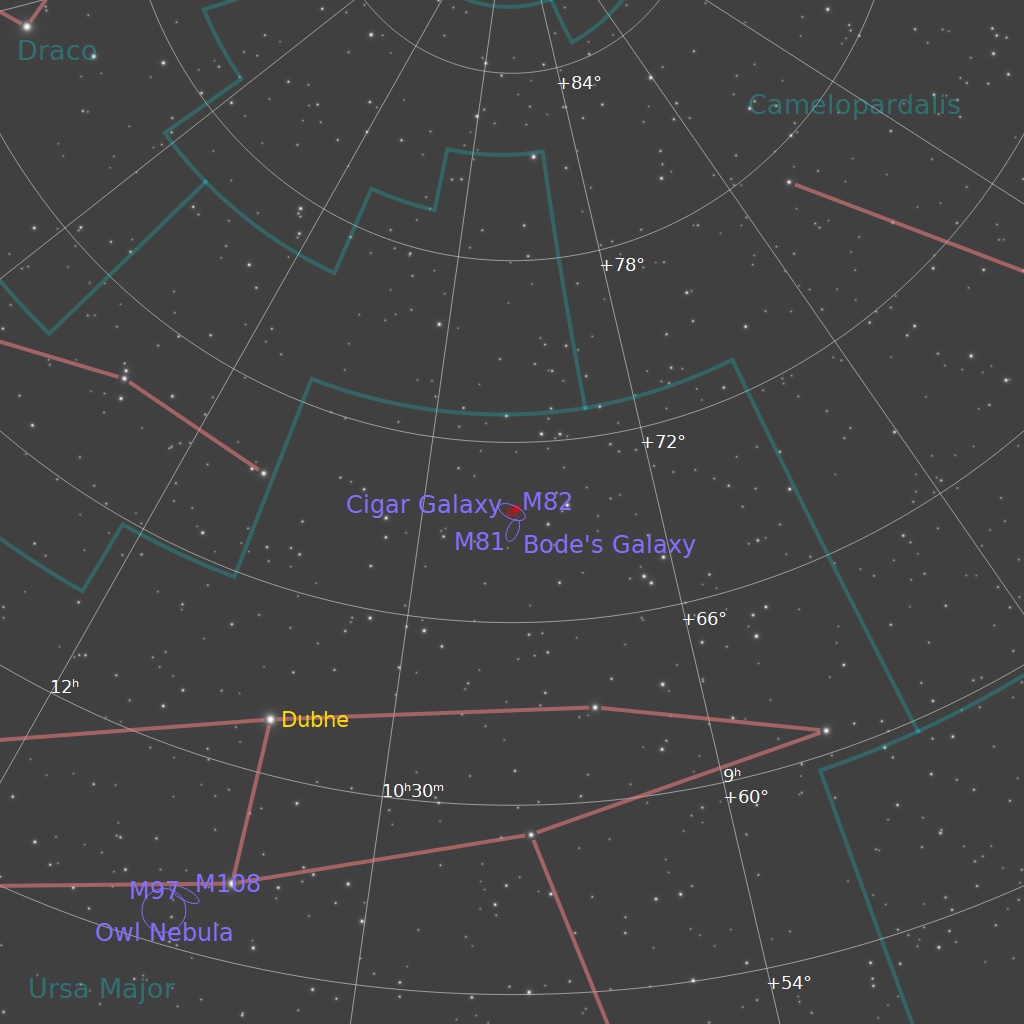
M82 lies about 11 to 12 million light years away, and has a diameter of almost 41,000 light years. It has a high rate of forming new stars, and is known as a starburst galaxy. It’s a neighbour of M81, lying just a million light years apart, as shown in this image of the two taken several years ago. A couple ofvery distant galaxies are identified in the annotated image of this field. I’ve presented this image with south up because I thought it looked best that way (most of my images are displayed with north up).
Tekkies:
Acquisition, focusing, and control of Paramount MX mount with N.I.N.A., TheSkyX and PHD2. Primalucelab low-profile 2″ Essato focuser and ARCO rotator. Guiding with PHD2. Equipment control with PrimaLuce Labs Eagle 4 Pro computer. All pre-processing and processing in PixInsight. Acquired from my SkyShed in Guelph. Data acquired under variable moonlight and average or worse transparency and seeing between February 19 – March 5, 2024.
Celestron 14″ EDGE HD telescope at f/11 (3,912 mm focal length) and QHY600M camera binned 2×2 with Optolong filters.
142 x 1m Red = 2hr 22m
140 x 1m Green = 2hr 20m
132 x 1m Blue = 2hr 12m
98 x 5m Ha = 8hr 10m
Total: 15hr 04m
Preprocessing: The WeightedBatchPreProcessing script was used to perform calibration, cosmetic correction, weighting, registration, local normalization and integration of all frames.
RGB master: A master RGB image was made from the Red, Green and Blue masters using ChannelCombination in RGB mode.
Gradient Removal: DBE was used to remove gradients from the RGB and Ha masters.
Colour Calibration: SpectroptometricColorCalibration was used to calibrate the RGB master.
Deconvolution: BlurXterminator was applied to the two masters with Automatic psf , star sharpening set to 0.4, and non-stellar set to 0.9.
Star Removal: StarXterminator was used to remove the stars from both masters, with default settings, except Large Overlap was selected. Only the RGB stars-only image was retained.
Linear Noise Reduction: NoiseXterminator was applied to the both masters with settings Amount=0.9 and Detail=0.25
Ha Continuum Subtraction: The ContinuumSubtraction script was used to remove continuum emissions from the Ha image.
Stretching: HistogramTransformation was applied to both masters to make pleasing images. Approximate background level after stretch was 0.08 for Ha and 0.10 for RGB.
Nonlinear Processing
Addition of Ha to RGB: PixelMath was used to blend the Ha master into the RGB image using the following expression with parameter values a=1.5 and b=0.10.
Red: max($T[0], a*Ha)
Green: $T[1]
Blue: iif($T[0]<a*Ha, $T[2] + b * Ha, $T[2])
Nonlinear Noise Reduction: NoiseXterminator was used to reduce noise in the background areas of both masters with Amount=0.9 and Detail=0.15.
Re-stretch: HistogramTransformation was used to boost contrast by moving the dark point to the toe of the histogram and slightly decreasing the mid-point slider.
Contrast Enhancement: LocalHistogramEqualization was applied twice. A Contrast Limit of 1.5 and 1 iteration was used for each LHE application (scale 40, strength 0.25; scale 125, strength 0.18).
Sharpening: MultiscaleMedianTransform was applied. (Layers 1 – 3 with strengths of 0.01, 0.06, and 0.07, respectively), using a mask to select only the galaxy.
Contrast, Brightness and Colour: Background and galaxy brightness, contrast, and saturation were adjusted in several iterations using CurvesTransformation with masks as required.
Stars-only steps: HistogramTransformation was applied to the RGB stars-only image. A mask was made by using ChannelExtraction to extract the luminance from the image. CurvesTransformation CIE c* slider was used to add boost colour in the stars through the star mask. A mask was made to select the largest stars and CurvesTransformation was used to make them a little smaller.
Star Restoration: PixelMath expression combine(starless, stars, op_screen()) was used to combine the starless HaRGB starless image with the stars-only image.
Final Steps: Background, galaxy, and star brightness, contrast, hue, and saturation were adjusted in several iterations using CurvesTransformation with masks as required. ICCProfileTransformation (sRGB IEC61966-2.1; Relative Colorimetric with black point compensation) was applied prior to saving as a jpg. The finder chart was made using the FindingChart process. The annotated version was made using the AnnotateImage script.







Leave A Comment