M51, The Whirlpool Galaxy
 Click image for full size version
Click image for full size version
April 5, 2024
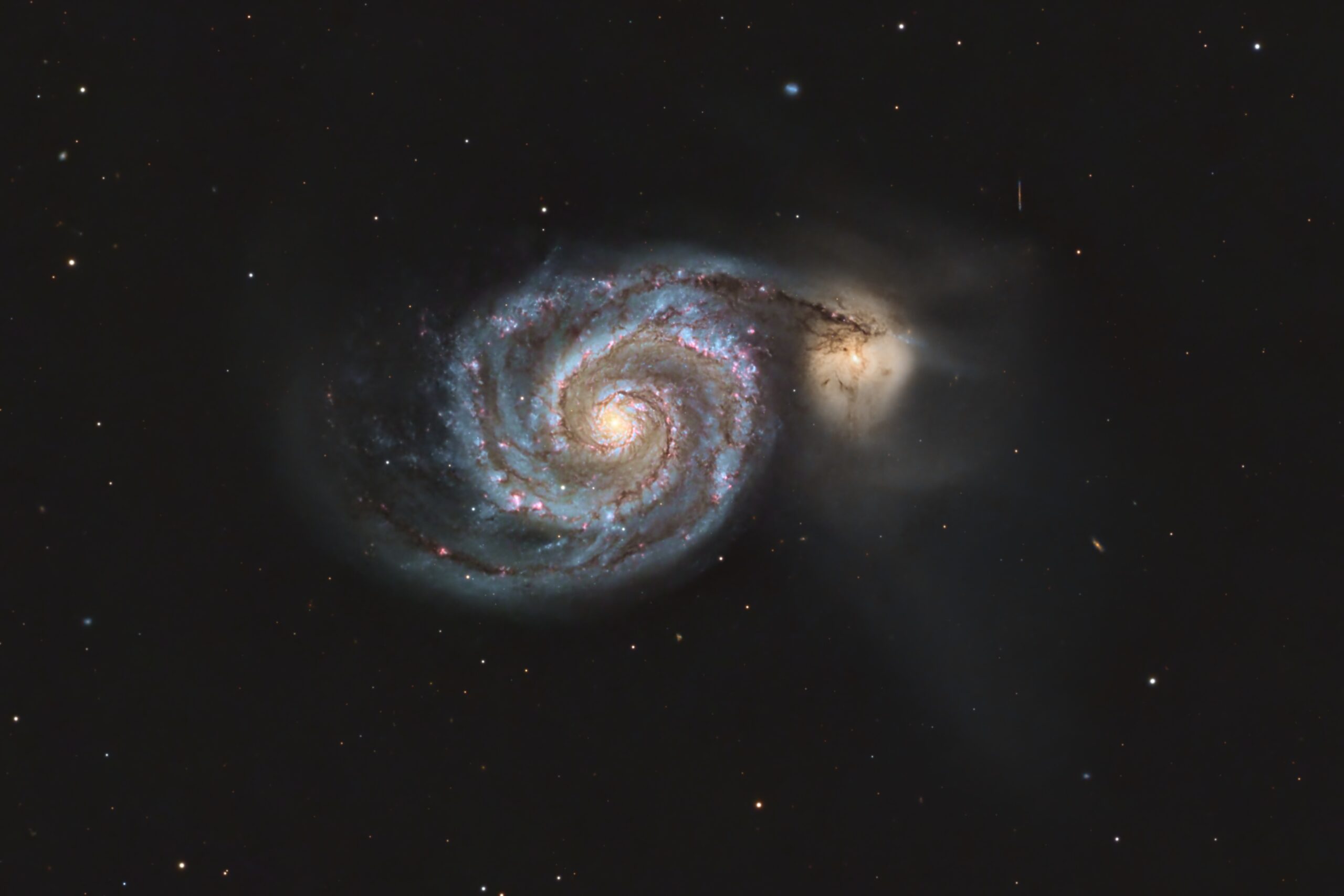
M51 is the galaxy in which spiral structure was first seen, by Lord Rosse in 1845 using a 72-inch telescope known as the “Leviathan of Parsonstown.” The galaxy was discovered in 1773 by Charles Messier. It’s fairly bright and I’ve seen it in binoculars in a reasonably dark sky.
To the right of the Whirlpool Galaxy in this image is NGC5195. The two are interacting, and you can see that the smaller galaxy has distorted M51’s arms. M51 has also smeared out its companion. The pair lie about 30 million light years away, beneath the end star of the handle of the Big Dipper. The Whirlpool Galaxy is about 60,000 light years across and has a mass of around 160 billion times that of our Sun. The pink features in M51 are emission nebulae, similar to the Rosette Nebula in our galaxy. The knots in the blue arms are star clusters, similar to M35 and NGC2158.
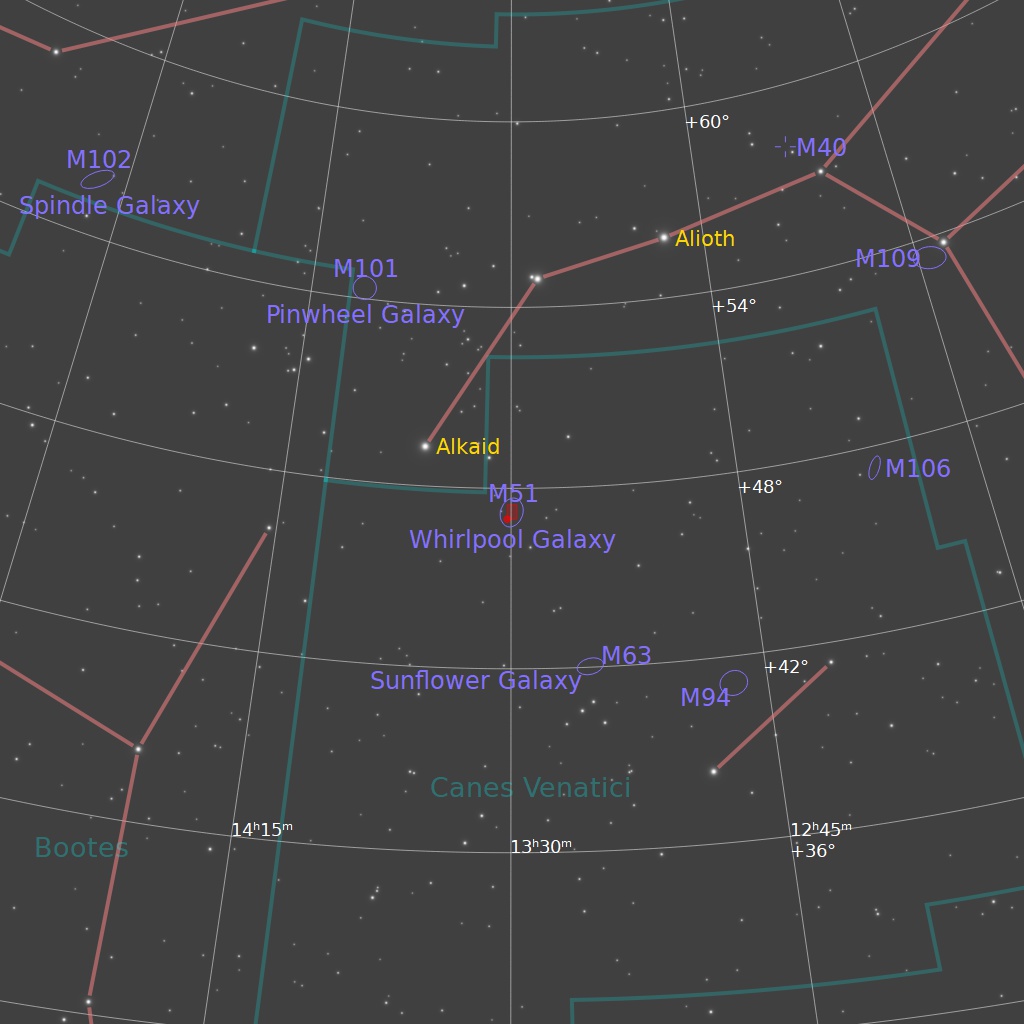
M51 and NGC5195 are the largest members of the M51 Group of galaxies. You can see several other members throughout this field. This group and two others (the M101 group and the NGC5866 group) may be part of a single, large, loose group of galaxies, since all lie at similar distances.
I have prepared an annotated image identifying the main galaxies (marked by ellipses), and also highlighting the locations of dozens of ancient quasars (marked by crosshairs), many of which lie more than 10 billion light years away. If you look closely you’ll find some of them in the crosshairs!
I imaged M51 in June 2021 with a 6″ refractor. The new version shows more detail, owing to the smaller pixels and much longer focal length of my current system.
Tekkies:
Acquisition, focusing, and control of unguided Paramount MX mount with N.I.N.A., TheSkyX. Primalucelab low-profile 2″ Essato focuser and ARCO rotator. Equipment control with PrimaLuce Labs Eagle 4 Pro computer. All pre-processing and processing in PixInsight. Acquired from my SkyShed in Guelph. Data acquired under variable moonlight and average transparency and seeing between March 12-30, 2024.
Celestron 14″ EDGE HD telescope at f/11 (3,912 mm focal length) and QHY600M camera binned 2×2 with Optolong filters.
113 x 1m Red = 1hr 53m
98 x 1m Green = 1hr 38m
110 x 1m Blue = 1hr 50m
29 x 1m Lum = 0hr29m
202 x 1m Ha = 3hr 22m
Total: 9hr 12m
Preprocessing: The WeightedBatchPreProcessing script was used to perform calibration, cosmetic correction, weighting, registration, local normalization, integration and Drizzle integration of all frames.
Gradient Removal: DBE was used to remove gradients from the all five masters.
RGB master: A master RGB image was made from the Red, Green and Blue masters using ChannelCombination in RGB mode.
Synthetic Luminance: A SynthL was made by integrating the five masters, weighted by SNR, with no pixel rejection
Colour Calibration: SpectroptometricColorCalibration was used to calibrate the RGB master.
Deconvolution: BlurXterminator was applied to the RGB, Ha and SynthL masters with Automatic psf , star sharpening set to 0.5, and non-stellar set to 0.5.
Star Removal: StarXterminator was used to remove the stars from the RGB, Ha and SynthL masters, with default settings, except Large Overlap was selected. The RGB and SynthL stars-only images were retained.
Linear Noise Reduction: NoiseXterminator was applied to the RGB, Ha and SynthL masters with settings Amount=0.9 and Detail=0.25
Ha Continuum Subtraction: The ContinuumSubtraction script was used to remove continuum emissions from the Ha image.
Stretching: HistogramTransformation was applied to the RGB, Ha and SynthL masters to make pleasing images. Approximate background level after stretch was 0.08 for Ha, 0.1 for SynthL and 0.09 for RGB.
Nonlinear Processing
Combinining SynthL and RGB: LRGBCombination was used to replace the lightness channel of the RGB image with the SynthL.
Saturation Boost: A mask was made using RangeSelection and used to select the galaxy, including the faintest regions. Curves was used to boost the saturation in the SynthLRGB master preparation for addition of Ha.
Addition of Ha to SynthLRGB: The NBRGBCombination script was used to combine the Ha with the SynthLRGB.
Nonlinear Noise Reduction: NoiseXterminator was used to reduce noise in the background areas of the SynthLHaRGB master with Amount=0.9 and Detail=0.15.
Re-stretch: HistogramTransformation was used to boost contrast by moving the dark point to the toe of the histogram and slightly decreasing the mid-point slider.
Contrast Enhancement: LocalHistogramEqualization was applied twice. A Contrast Limit of 1.5 and 1 iteration was used for each LHE application (scale 40, strength 0.2; scale 125, strength 0.15).
Sharpening: MultiscaleMedianTransform was applied. (Layers 1 – 6 with strengths of 0.01, 0.02, 0.02, 0, 0, and 0.02, respectively), using a mask to select only the brighter portions of the galaxy.
Contrast, Brightness and Colour: Background and galaxy brightness, contrast, and saturation were adjusted in several iterations using CurvesTransformation with masks as required.
Stars-only steps: HistogramTransformation was applied to the RGB and SynthL stars-only images. They were combined as for the starless images using LRGBCombination. The SynthL stars-only was used as a mask and CurvesTransformation saturation slider was used to boost colour in the stars.
Star Restoration: PixelMath expression combine(starless, stars, op_screen()) was used to combine the starless SynthLHaRGB starless image with the stars-only image.
Final Steps: Background, galaxy, and star brightness, contrast, hue, and saturation were adjusted in several iterations using CurvesTransformation with masks as required. ICCProfileTransformation (sRGB IEC61966-2.1; Relative Colorimetric with black point compensation) was applied prior to saving as a jpg. The finder chart was made using the FindingChart process. The annotated version was made using the AnnotateImage script.







Very nice image, Ron! A lot of time, but worth it.
Quick question: Why unguided? Not needed with that mount or actually detrimental?
Not needed with that mount for exposures up to about 10m – when the mount is very well polar aligned and the T-Point model and Periodic Error Correction are set up. Guiding isn’t detrimental; it’s just one more thing that can go wrong.
Gorgeous image! The time and expertise put in is incredible!